You can access your Azure IaaS virtual machine (VM) in multiple ways like SSH or RDP, depending on your operating system and configuration. However, if you have issues with the RDP or SSH network configuration, you need to have a way to troubleshoot your virtual machine (VM). Luckily Azure offers you different management tools to work with Azure VMs for automation or troubleshooting. With the Run Command can run a PowerShell or shell script within an Azure VM remotely by using the VM agent. This scenario is especially useful when you need to troubleshoot operating system network configurations or user access configuration. For example, it can be convenient to reset RDP configurations on Windows Server virtual machines.
You use Run Command for Azure VMs through the Azure portal, REST API, Azure CLI, or PowerShell. Here are some examples:
Azure VM Run Command in the Azure Portal
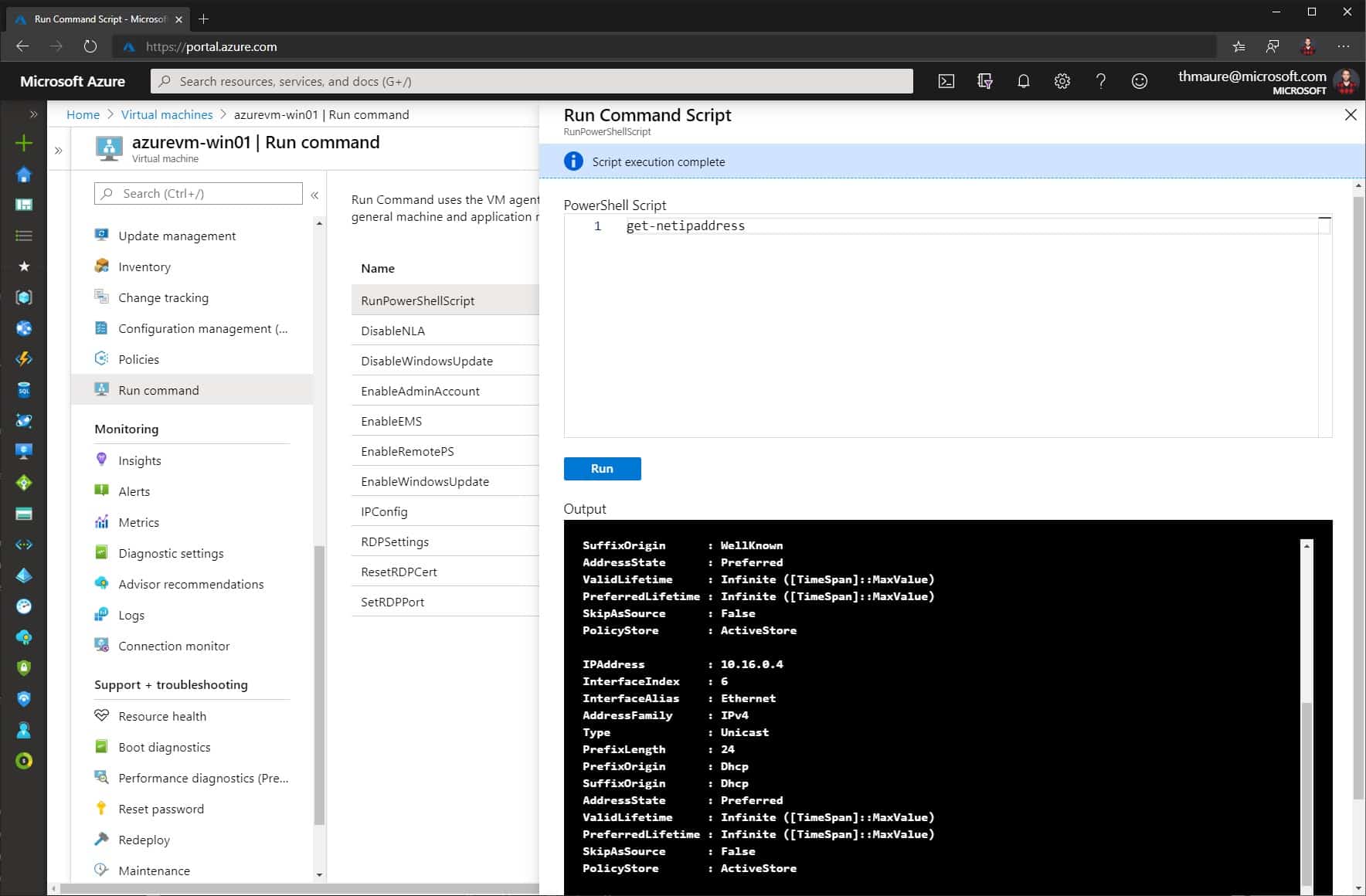
You can run the command directly from the Azure Portal. In the menu of the Azure VM, you can select Run command. Here you can find some predefined scripts to troubleshoot your Azure VM. In the case of a Windows VM, you will find scripts like configuring RDP port or enable PowerShell remoting. But you can also run your custom PowerShell script.
For Linux VMs, you will find predefined options to run a Linux shell script or ifconfig to list the network configuration.
Azure CLI
You also run commands directly from the Azure CLI using the following command:
az vm run-command invoke -g myResourceGroup -n myVm --command-id RunShellScript --scripts "sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y nginx"
This “az vm run-command” CLI command works with Linux and Windows VMs on Azure. You can find more information about the Azure CLI option here.
You can also run the Azure CLI directly from Cloud Shell. You can learn more about the Azure Cloud Shell on my blog: Mastering Azure with Cloud Shell.
Azure PowerShell
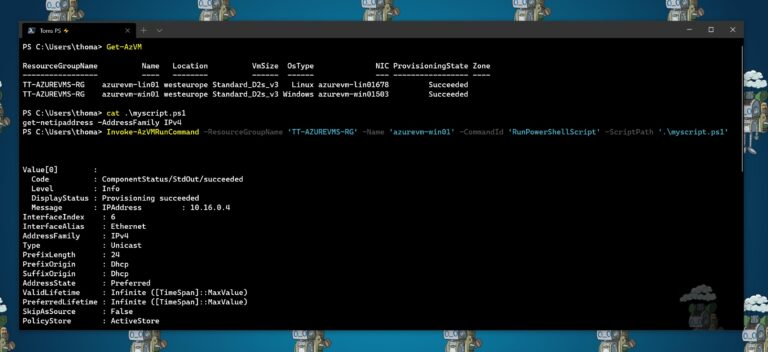
You can also use Azure PowerShell to use the run command capabilities to run PowerShell scripts against the guest agent inside the Azure VM. For that, you can simply use the Invoke-AzVMRunCommand cmdlet from the Az PowerShell module.
You can also run this command directly from Azure Cloud Shell as well.
Invoke-AzVMRunCommand -ResourceGroupName '<myResourceGroup>' -Name '<myVMName>' -CommandId 'RunPowerShellScript' -ScriptPath '<pathToScript>' -Parameter @{"arg1" = "var1";"arg2" = "var2"}
The cmdlet expects the script referenced in the -ScriptPath parameter to be local to where the cmdlet is being run. If you are running it from your local machine, the script will need to be stored on your machine. If you are running the script from Cloud Shell, you will need to have the script available in your Cloud Shell. You can find more information about the Invoke-AzVMRunCommand PowerShell cmdlet option here.
Quick side note, with PowerShell 7, you can also run PowerShell Remoting over SSH.
Conclusion
The Run Command option is a great solution if you need to run scripts inside an Azure VM using the guest agent to troubleshoot network or access configurations. If you want to learn more, you can find more about the Run Command here on Microsoft Docs.
You can also find more information about the Azure Virtual Machine guest agent here:
I hope this blog post was helpful and provides you a great overview of how you can run commands against your Azure VMs, especially in troubleshooting scenarios. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave a comment. I am always looking for new helpful content, so if you have any ideas of articles or videos, please reach out to me using the comments and I will see what I can do.
Tags: Azure, Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Azure VM, Bash, CLI, command, IaaS, Microsoft, Portal, PowerShell, RDP, Run, run command, script, SSH, Troubleshooting, Virtual Machine, VM Last modified: March 8, 2021









It would be nice to have the possibility to save the script to reuse them when needed. Something for the DEV team 😉
That’s pretty cool, but also could be problematic if say, the wrong person had access to the azure VM because of a permissions mishap. Is there a way to disable that (in the azure portal or otherwise), out of curiosity?
Will this also work for Azure Arc Server?
Thanks TM. Is it possible to inject some AD credentials for the script that gets run on the target VM, to use? For example, the script on the target VM needs to be able to create AD computer accounts as part of its process, however the credentials that get used for the Invoke-AzVmRunCommand are not domain credentials, they are an Azure Subscription context, so not domain-aware, and therefore the target script runs, but then fails when trying to create AD objects, with access denied. Thanks