Around 4 years ago I wrote a blog post about how to Replace netsh with Windows PowerShell which includes basic powershell networking cmdlets. After working with Microsoft Azure, Nano Server and Containers, PowerShell together with networking becomes more and more important. I created this little cheat sheet so it becomes easy for people to get started.
Basic Networking PowerShell cmdlets
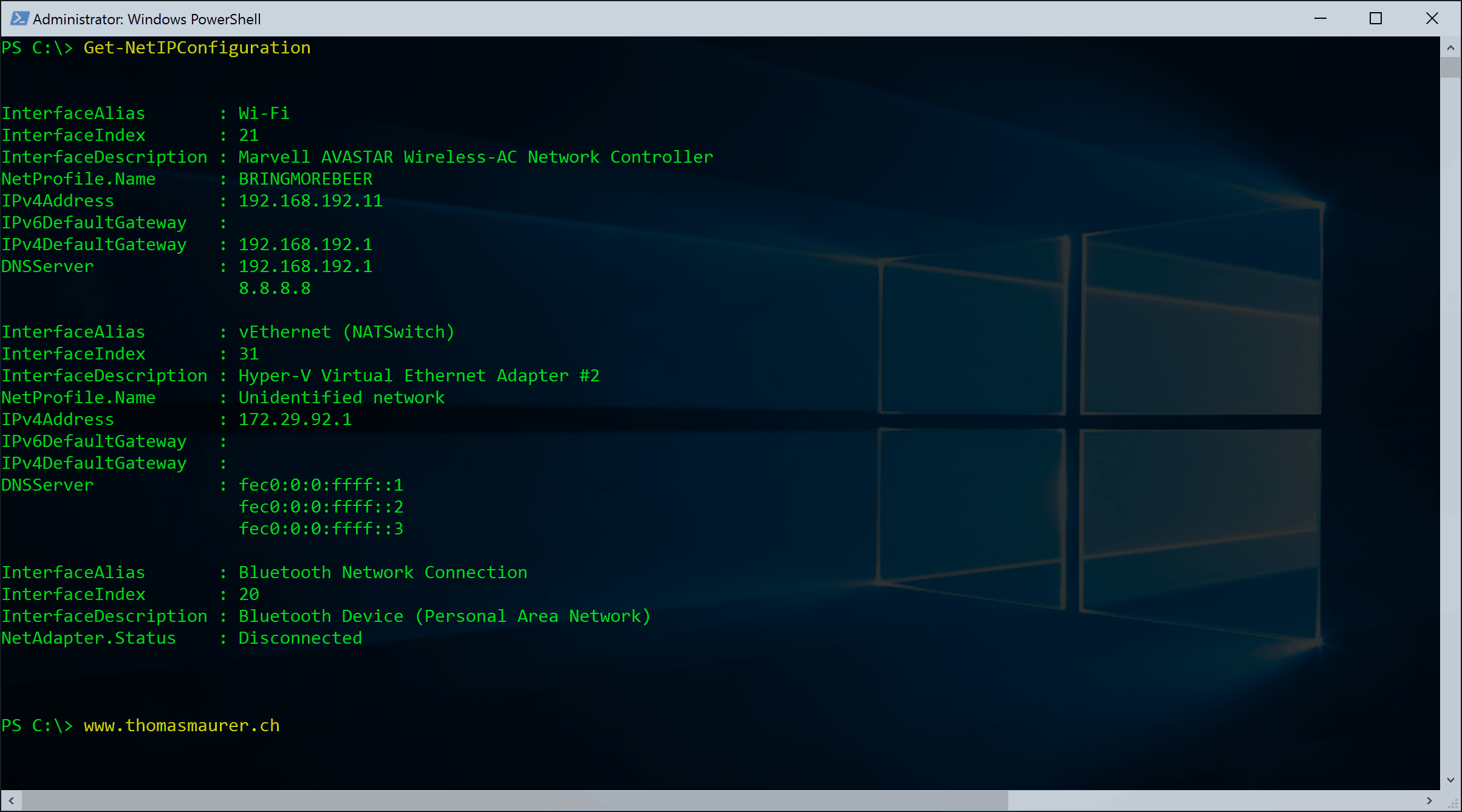
Get the IP Configuration (ipconfig with PowerShell)
Get-NetIPConfigurationList all Network Adapters
Get-NetAdapterGet a spesific network adapter by name
Get-NetAdapter -Name *Ethernet*
Get more information VLAN ID, Speed, Connection status
Get-NetAdapter | ft Name, Status, Linkspeed, VlanID
Get driver information
Get-NetAdapter | ft Name, DriverName, DriverVersion, DriverInformation, DriverFileName
Get adapter hardware information. This can be really usefull when you need to know the PCI slot of the NIC.
Get-NetAdapterHardwareInfoDisable and Enable a Network Adapter
Disable-NetAdapter -Name "Wireless Network Connection" Enable-NetAdapter -Name "Wireless Network Connection"
Rename a Network Adapter
Rename-NetAdapter -Name "Wireless Network Connection" -NewName "Wireless"
IP Configuration using PowerShell
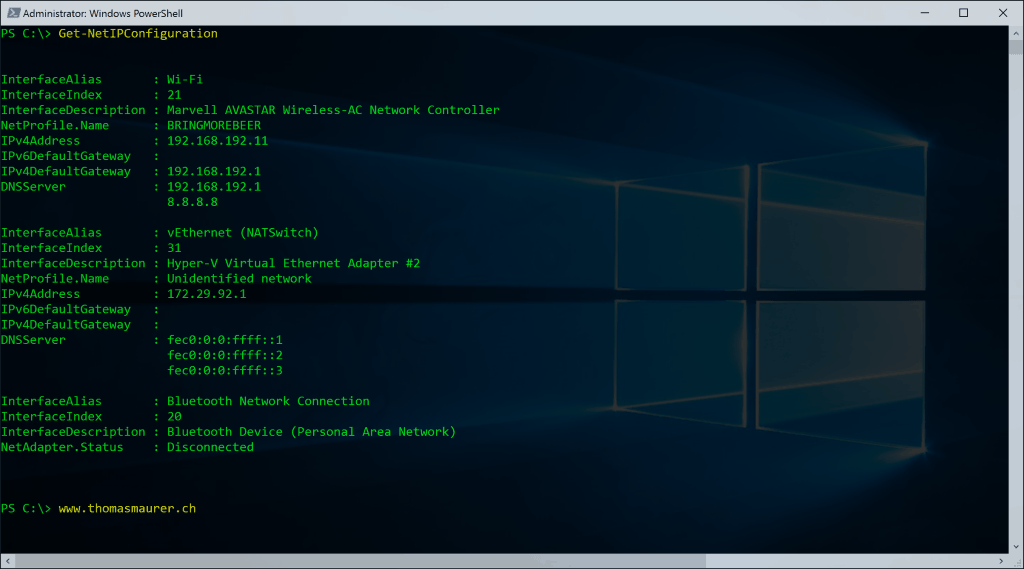
Get IP and DNS address information
Get-NetAdapter -Name "Local Area Connection" | Get-NetIPAddress
Get IP address only
(Get-NetAdapter -Name "Local Area Connection" | Get-NetIPAddress).IPv4Address
Get DNS Server Address information
Get-NetAdapter -Name "Local Area Connection" | Get-DnsClientServerAddress
Set IP Address
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias "Wireless" -IPv4Address 10.0.1.95 -PrefixLength "24" -DefaultGateway 10.0.1.1
or if you want to change a existing IP Address
Set-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias "Wireless" -IPv4Address 192.168.12.25 -PrefixLength "24"
Remove IP Address
Get-NetAdapter -Name "Wireless" | Remove-NetIPAddress
Set DNS Server
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias "Wireless" -ServerAddresses "10.10.20.1","10.10.20.2"
Set interface to DHCP
Set-NetIPInterface -InterfaceAlias "Wireless" -Dhcp Enabled
Clear DNS Cache with PowerShell
You can also manage your DNS cache with PowerShell.
List DNS Cache:
Get-DnsClientCacheClear DNS Cache
Clear-DnsClientCachePing with PowerShell
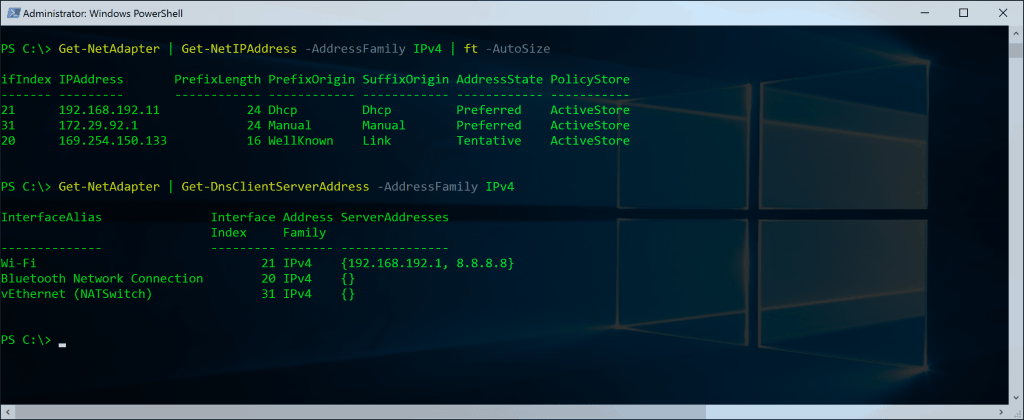
How to Ping with PowerShell. For a simple ping command with PowerShell, you can use the Test-Connection cmdlet:
Test-Connection thomasmaurer.chThere is an advanced way to test connection using PowerShell
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName www.thomasmaurer.ch
Get some more details from the Test-NetConnection
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName www.thomasmaurer.ch -InformationLevel Detailed
Ping multiple IP using PowerShell
1..99 | % { Test-NetConnection -ComputerName x.x.x.$_ } | FT -AutoSize
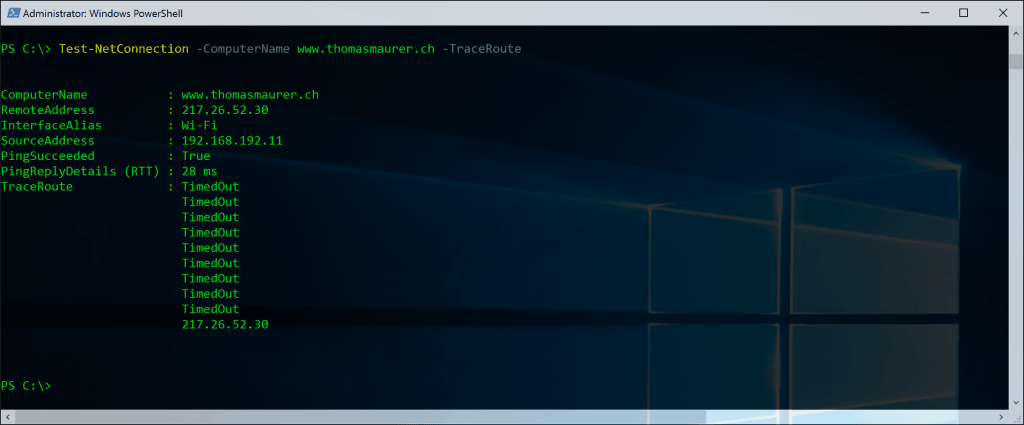
Tracert
Tracert with PowerShell
Test-NetConnection www.thomasmaurer.ch –TraceRoutePortscan with PowerShell
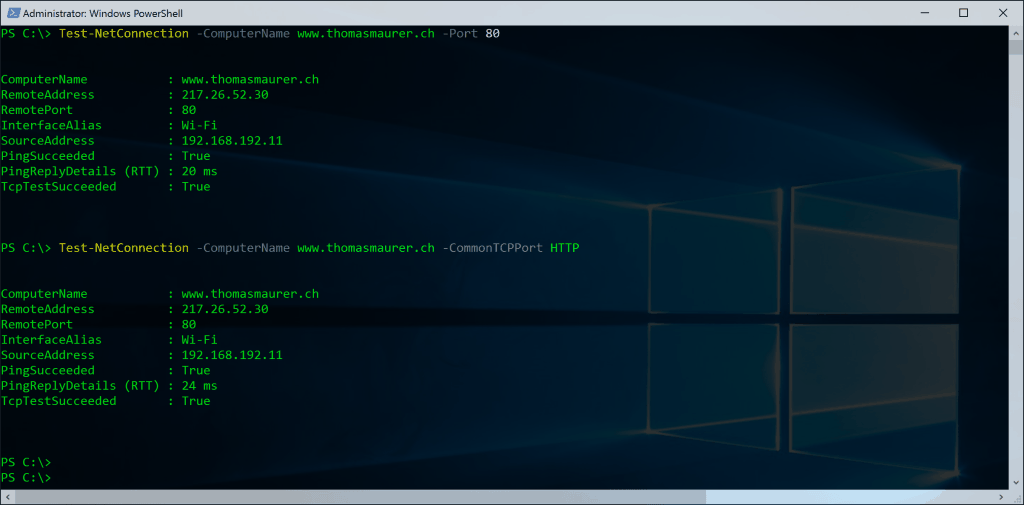
Use PowerShell to check for open port
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName www.thomasmaurer.ch -Port 80 Test-NetConnection -ComputerName www.thomasmaurer.ch -CommonTCPPort HTTP
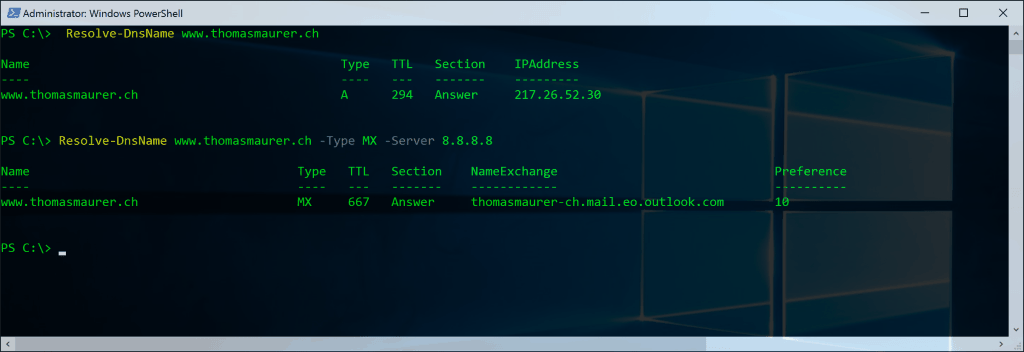
NSlookup in PowerShell
NSlookup using PowerShell:
Resolve-DnsName www.thomasmaurer.ch Resolve-DnsName www.thomasmaurer.ch -Type MX -Server 8.8.8.8
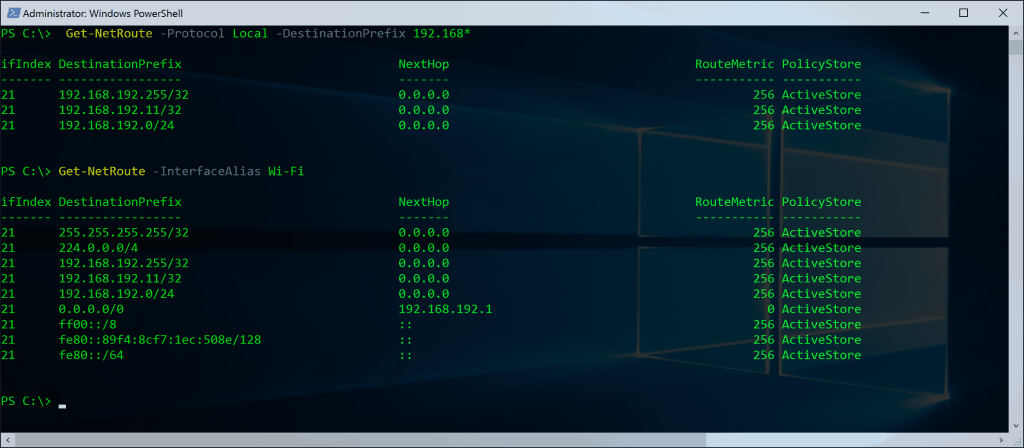
Route in PowerShell
How to replace Route command with PowerShell
Get-NetRoute -Protocol Local -DestinationPrefix 192.168* Get-NetRoute -InterfaceAlias Wi-Fi New-NetRoute –DestinationPrefix "10.0.0.0/24" –InterfaceAlias "Ethernet" –NextHop 192.168.192.1
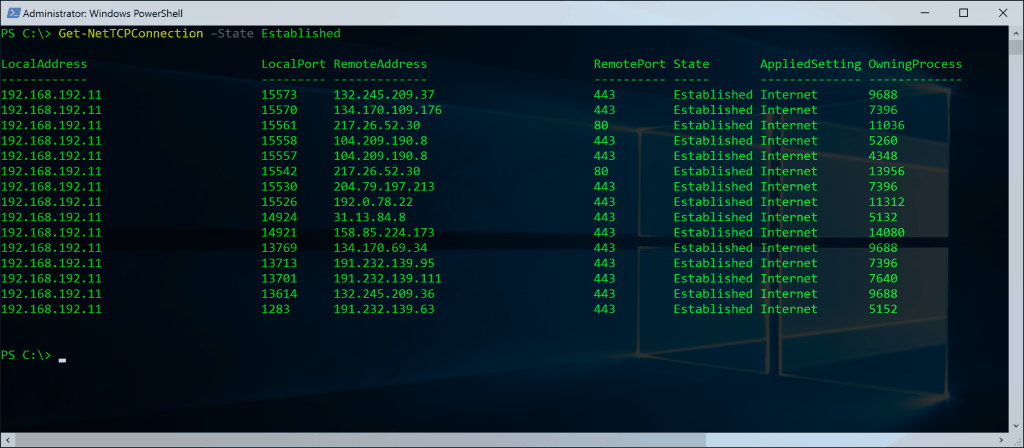
NETSTAT in PowerShell
How to replace NETSTAT with PowerShell
Get-NetTCPConnection Get-NetTCPConnection –State Established
NIC Teaming PowerShell commands
Create a new NIC Teaming (Network Adapter Team)
New-NetLbfoTeam -Name NICTEAM01 -TeamMembers Ethernet, Ethernet2 -TeamingMode SwitchIndependent -TeamNicName NICTEAM01 -LoadBalancingAlgorithm Dynamic
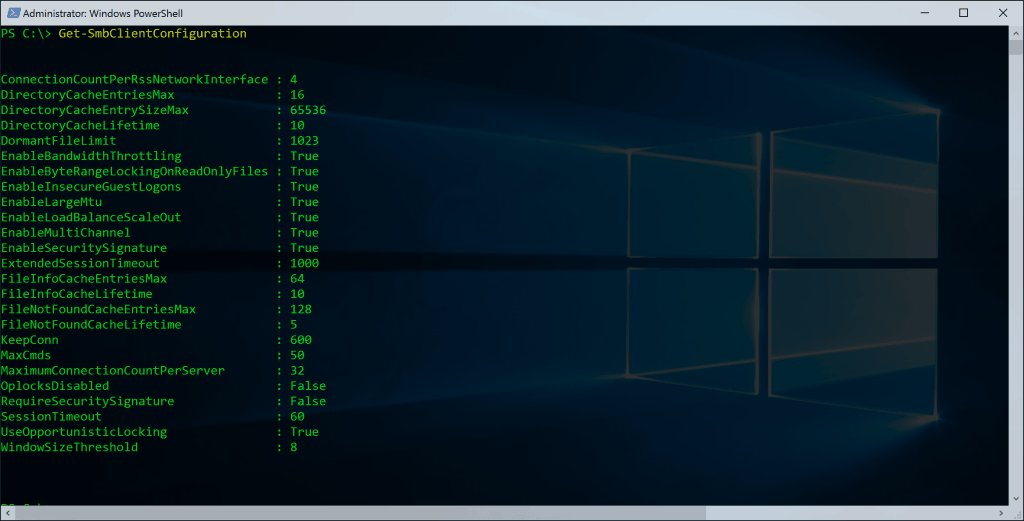
SMB Related PowerShell commands
Get SMB Client Configuration
Get-SmbClientConfigurationGet SMB Connections
Get-SmbConnectionGet SMB Mutlichannel Connections
Get-SmbMutlichannelConnectionGet SMB open files
Get-SmbOpenFileGet SMB Direct (RDMA) adapters
Get-NetAdapterRdmaHyper-V Networking cmdlets
Get and set Network Adapter VMQ settings
Get-NetAdapterVmq # Disable VMQ Set-NetAdapterVmq -Enabled $false # Enable VMQ Set-NetAdapterVmq -Enabled $true
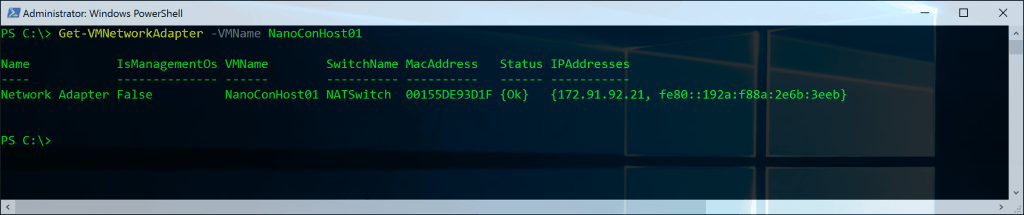
Get VM Network Adapter
Get-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName Server01
Get VM Network Adapter IP Addresses
(Get-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName NanoConHost01).IPAddresses
Get VM Network Adapter Mac Addresses
(Get-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName NanoConHost01).MacAddress
I hope you enjoyed it and the post was helpful, if you think something important is missing, please add it in the comments.
Tags: Azure, DNS, Hyper-V, IP, IP Address, Microsoft, Microsoft Azure, Netstat, Network, Network Adapter, Networking, Networking PowerShell cmdlets, nslookup, Ping, PowerShell, SMB, Tracert, Windows, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 Last modified: January 23, 2019








Hi Thomas,
Great blog! Keep up the good work.
I found a little error in on of your lines:
Ping multiple IP using PowerShell
1..99 | % { Test-NetConnection -ComputerName http://www.thomasmaurer.ch } | FT -AutoSize
Dit should be:
1..99 | % { Test-NetConnection -ComputerName x.x.x.$_ } | FT -AutoSize
Otherwise it wil ping the same computername 99 times. :)
Best regards,
Alain
Thanks :) Fix it
Great work. Informative post.
On thing that I havent found any where that looked is a replacement on PS for “ipconfig /release/renew”, any idea?
Hi,
I would really love to see a print function for your website.
Printing this cheat-sheet to pin it besides my desk is not going to work with a lot of effort.
Thanks
Very helpful collection Thomas, thank you.
Great set of articles. I do have one question: where is there support in PowerShell for ‘hostednetwork’? The context for my question can be found on superuser.com in /questions/1141404/how-does-one-automate-the-setting-up-of-a-windows-10-wireless-hotspot-using-powe
Any pointers to the PS equivalent of netsh show sslcert ?
Very cool!
thanks :)
Old post, but what about commands for examlple: netsh lan add profile filename=”somefilething.xml” interface=”Ethernet” or netsh lan set eapuserdata filename=”somefile.XML” allusers=yes interface=”Ethernet”
This is really helpful cheat sheet, i have managed to fix the error on 1..99 | % { Test-NetConnection -ComputerName x.x.x.$_ } | FT -AutoSize, i have used the real IP address(-ComputerName 192.168.8.1.$_} | FT -Autosize it works perfectly.
Thanks alot Geeks you save us big time
Excellent commands thank you for putting this together
Thank you for the feedback :)
You’re welcome
Its very useful cmdlets . Your little try to do best for others, is helps lot of people . Great work 👍