
The reason for this blog post was a lecture I had at university where lecturer talked about ERP systems (enterprise resource planning) and a question came up from one of the other students about ERP in the cloud and how Cloud Computing is defined. I am not really happy with the answer he gave, because the answer was totally focused on Software as a Service hosted from a service provider and accessible over the internet. Well this is a part of cloud computing but doesn’t not really cover the real definition.
I know I will maybe get a lot of comments on this post, because there is no official definition of “Cloud Computing” and every company maybe thinks different about it, depending on their product range
As someone who has worked in the hosting business and now is working as a consultant for mostly building private or hosted private clouds the definition looks really different. One important statement first. Virtualization is not Cloud Computing, virtualization is a great enhancement for Cloud Computing and is also a important enabler of Cloud computing because without virtualization Cloud Computing could be really hard to do.
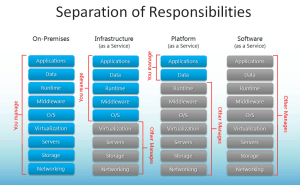
I my opinion Cloud Computing is not a technology, Cloud Computing is a concept you can use to provide access to resources. There are three different scenarios in cloud computing.
Image Source: blogs.technet.com
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service – IaaS basically allows customers to use compute, storage and networking resources and deploy for example virtual machines with full access to the operating system. (Example: Windows Azure, Amazon,…)
- Platform-as-a-Service – PaaS provides customers with a platform for their application, for example Windows Server with IIS where customers can deploy their application but don’t have to think about the server itself. (Example: Windows Azure, Webhosting Providers,…)
- Software-as-a-Service – SaaS allows customer to use just a software without caring about the installation or platform itself. For example hosted mailservers or CRMs (Example: Office365, Microsoft Dynamics Online, Xbox Live, Outlook.com,…)
Well another common mistake is to think cloud is always hosted in the internet. Since Cloud Computing is a concept to deliver services, companies can do this also internally which is mostly known as Private Cloud. The Private Cloud can of course also be IaaS, PaaS or SaaS and could be accessible from the internet, but it could also only be available company internal.
- Public Cloud – The Public Cloud is maybe the Cloud people think of mostly when they are talking about Cloud Computing. This is mostly shared services hosted from a services provider which is accessible from the internet.
- Private Cloud – The Private Cloud is a Cloud made for a just one customer or company for example this could be an on premise Cloud hosted in my own datacenter. In some cases the Private Cloud could also be hosted from a services provider.
- Hybrid Cloud – The Hybrid Cloud model will be the model a lot of companies will go for, or already did even without knowing about it. The Hybrid Cloud is a scenario where I have a Private Cloud hosted on premise in my datacenter but I also extend my Cloud to the Public Cloud by connecting cloud services such as Windows Azure or Office 365 to my Private Cloud.
I already wrote about 500 words, but I still didn’t not really answers the question what Cloud Computing is, so we going to have a look at Wikipedia:
Cloud computing – correctly: a Computing Cloud – is a colloquial expression used to describe a variety of different computing concepts that involve a large number of computers that are connected through a real-time communication network (typically the Internet). Cloud Computing is a jargon term without a commonly accepted non-ambiguous scientific or technical definition. In science Cloud computing is a synonym for distributed computing over a network and means the ability to run a program on many connected computers at the same time. The popularity of the term Cloud computing can be attributed to its use in marketing to sell hosted services in the sense of Application Service Provisioning that run Client server software on a remote location.
So with this definition there are five common properties every Cloud has, doesn’t matter if it’s IaaS, PaaS or SaaS based or hosted in the Private or Public Cloud.
- Elastic and Scalable – I think this is one of the overall parts of a cloud. It’s important to be very flexible to get new resources if your business grows over time or has some special peaks where you need more resources. Resources could be more compute power, more virtual machines, more users, or more mailboxes.
- Pooled Compute Resources – From a cloud provider perspective I want to pool my compute, storage and network resources and share them for different customers or services.
- Provides Self-Service Provisioning – To request new resources (virtual machines, Mailboxes or whatever) over a self-service portal which automatically kicks of the specific tasks.
- Highly Automated Management – Because we want to use Self-Services provisioning and doing this in large scales, it’s important that the environment is highly automated. If you think about a simple example: A new employee starts at your company and you want to create a new mailbox for him, you can create a it over a self-services portal. The creation of the mailbox has to me automated in the background because you don’t want to wait for someone to create the mailbox manually maybe two days later.
-
Usage-Based Chargeback – Trough the pooled resource you want to be able to do chargeback based on consumed resources. Even if you do another billing system you still want to know how much resources customers have used. This could be how many mailboxes did I use last month, how many minutes my virtual machines was running this month, or much disk space did I use.
I think this 5 things do cover the properties of Cloud Computing in basically all the common scenarios. This there are a lot of things I did not cover in my blog post but it should help people which are new to cloud computing help to understand the different scenarios.
Tags: Amazon, Azure, Cloud, Cloud Computing, Definition of Cloud Computing, Hybrid Cloud, IaaS, MAS, MASBEM, Microsoft, Office 365, PaaS, Private Cloud, Public Cloud, SaaS, University, Virtualization, Windows Azure Last modified: January 7, 2019







Well done Thomas!. IMHO your explanation should go to Wikipedia and should be a mandatory read for every CEO/CIO and all others talking the whole day about clouds.
:-)
Thanks for this article! :D
Hi Thomas,
Thank you for the article.
I found it very useful.
I might be wrong but I think I find a typo:
“The creation of the mailbox has to me automated…”
me should be a be if I am not mistaken.
Best regards