System Center Virtual Machine Manager brings a cool new feature called Bare Metal Deployment. This feature allows deploying new Hyper-V hosts via Out-of-Band Management (IPMI or SMASH) with the Virtual Machine Manager. In my lab environment I use Cisco UCS C200 M2 servers as my Hyper-V servers but this guide will also work with servers from other vendors such as HP, IBM or Dell.
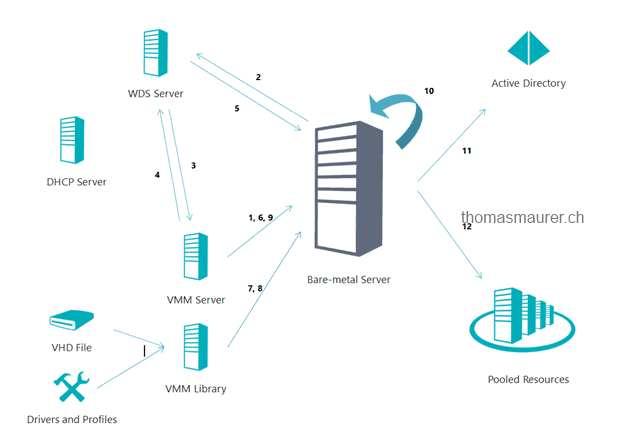
Deployment Process
- SCVMM boots up Bare-Metal Server via OBM
- Send PXE Boot requests
- WDS asks SCVMM for authorize PXE boot
- SCVMM approves
- Boot Windows PE
- Run pre GCE scripts to configure Raid and other settings
- Copy the VHD from VMM Library
- Get drivers
- Run post GCE scripts to do additional configurations
- Doing post configuration
- Domain join
- Adding server to the resource pool
Configure Deployment
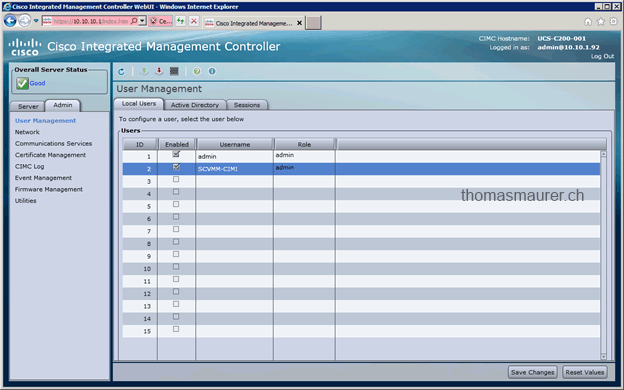
As step one you have to configure the out-of-band management of your server. Vendors offer different Base-Board Management Controllers (BMC) which allows users to shut down or start the physical server. Cisco calls it CIMI (Cisco Integrated Management Interface), HP calls it iLO and Dell calls I DRAC. I created a special user on the CIMI for the Virtual Machine Manager Run As account. In my case I had to create a new user with the admin user role, because the normal user role had not enough rights to shut down and start the physical server.
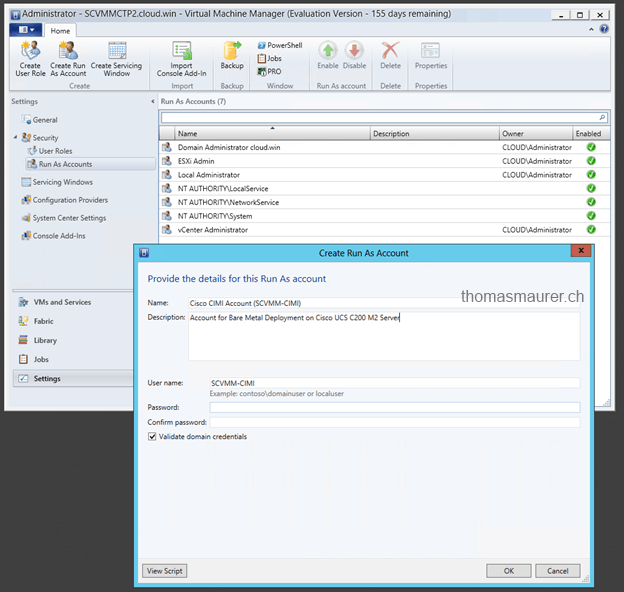
After I created this user I added the user as Run As account in SCVMM.
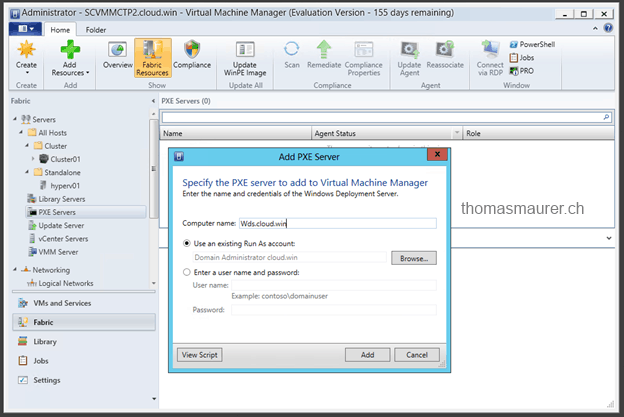
After I added the new Run As account I added my Windows Deployment Server (WDS) as PXE server in the SCVMM console. If you are not already using a WDS server in your environment you can simply setup one by adding the WDS role to a server and doing the basic configuration. You don’t need to add any images on the WDS server, SCVMM will take care of that.
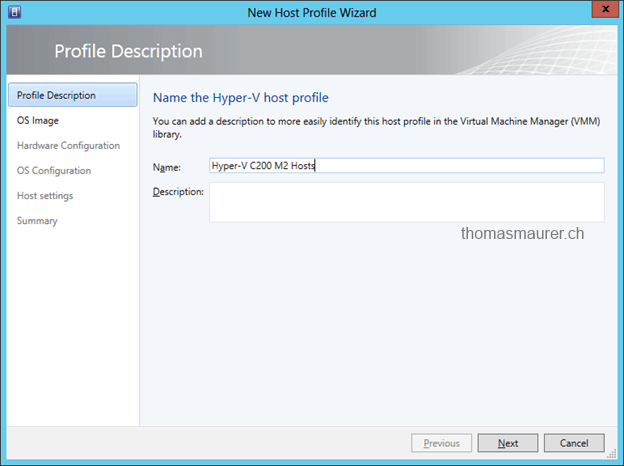
Next, a Host Profile for the Hyper-V Servers has to be created. In the Virtual Machine Manager Library you have to create a new Host Profile.
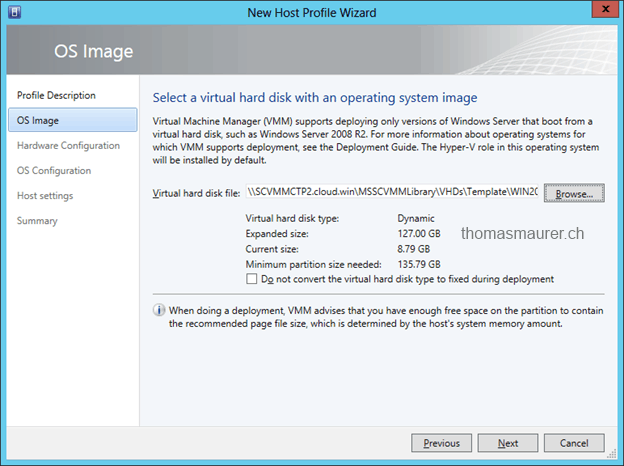
Choose the VHD in your SCVMM Library which should be deployed on as the Hyper-V Host Operating System.
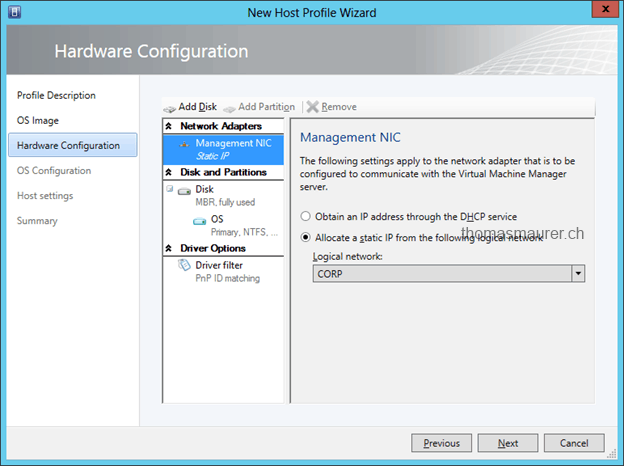
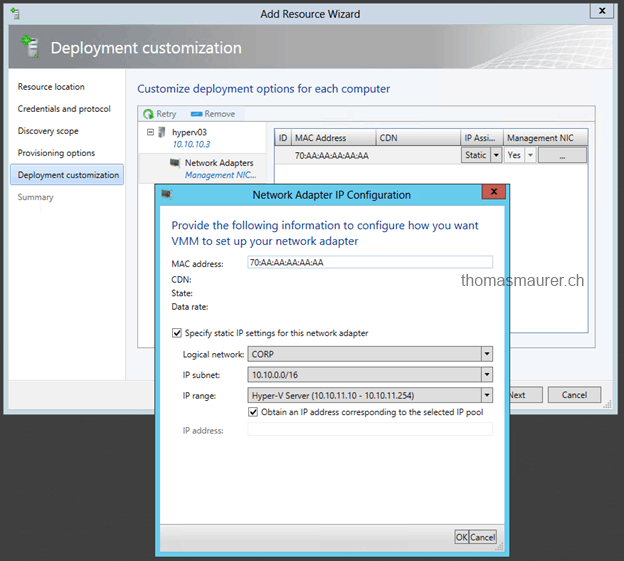
Configure some other settings for your Hyper-V Host, for example the Management Network Interface.
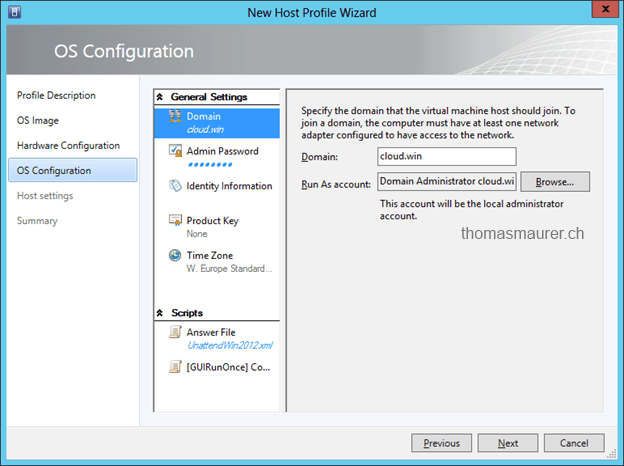
In the next step you have to configure some other settings of the Hyper-V Host. For example in Domain, Admin Password, Time Zone etc. You should also add a Unattended XML Answer File which allows you to do a deeper configuration of the Host Operating System.
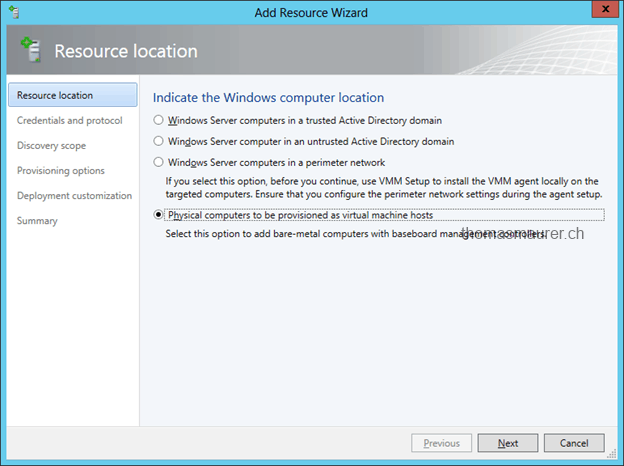
After you have created the Hyper-V Host Profile you can now add new Hyper-V Hosts Servers. In the Add Resource Wizard select Physical computers and follow the wizard.
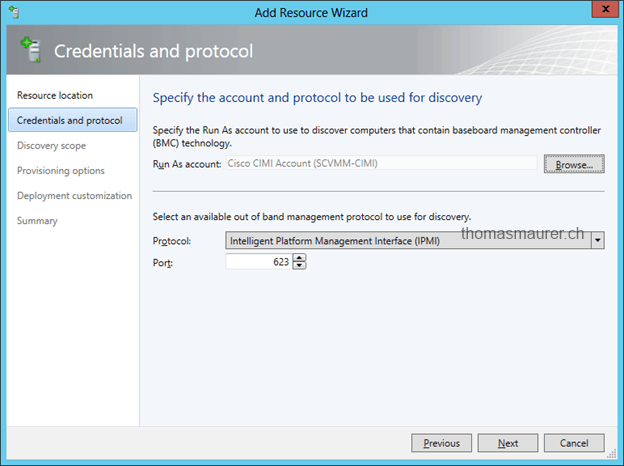
First choose the credentials and the protocol. As credentials I use the Run As account I have created before and the Cisco CIMI supports IPMI.
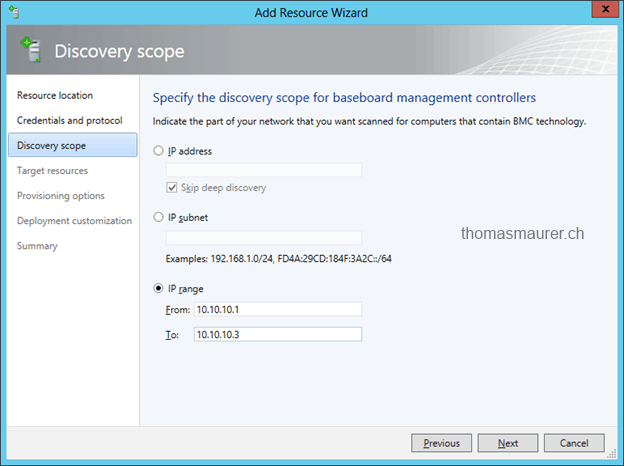
Now I scan the range of BMC IP address of my Hyper-V Host servers.
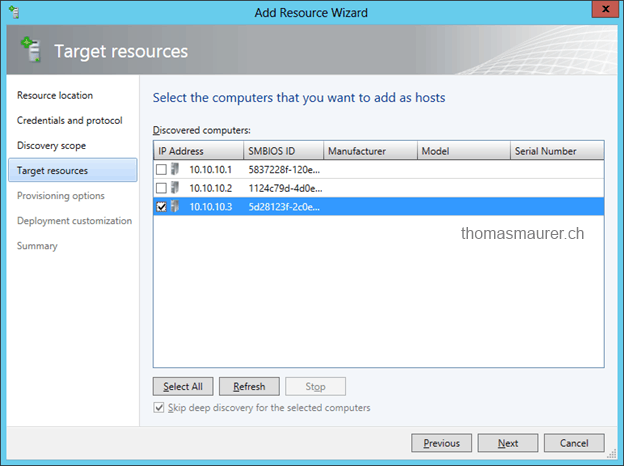
I select the server physical server which I want to deploy as a new Hyper-V host. Make sure it is the right hosts, otherwise you will take down the wrong server.
I have to select the management network interface. In SCVMM 2012 I need the MAC address of this NIC. In SCVMM 2012 SP1 this screen has changed a little. In CTP2 of SCVMM 2012 SP1 I can see some of the new possibilities which will come in Service Pack 1 for System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012, for example CDN (Consisted Device Naming).
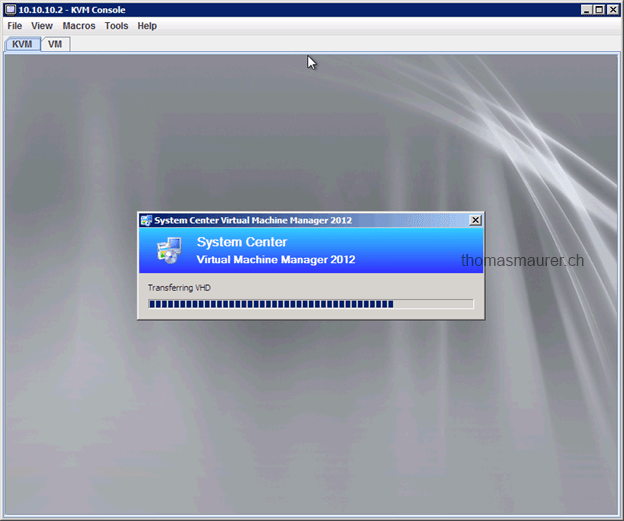
After you started the installation you can watch the installation process. In my lab this took around 45 minutes to deploy the host from bare metal to a domain joined Hyper-V host.
I hope this guide gives you a small insight in the System Center Virtual Machine Manager Bare-Metal Deployment.
Tags: Bare-metal, BMC, C200 M2, CIMI, Cisco, Cisco UCS, Hyper-V, Microsoft, PXE, SCVMM, System Center, UCS, Virtual Machine Manager, VMM, Windows Server, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 Last modified: August 21, 2012








Interesting post, nice one Thomas, I am wondering how the RAID will be configured ?!
Hi
Yes sure you could use some pre deployment scripts with command line raid utilities.