In Windows Server 2012 Microsoft introduced Cluster-Aware Updating or short CAU. Cluster-Aware Updating allows you to update your cluster nodes via automated workflow. Maybe you are familiar with the Remediation process in System Center Virtual Machine which allows you to automatically set a Hyper-V node in maintenance mode, move Virtual Machines to another node, install patches on your Hyper-V Cluster node and bring the node back online. CAU can do the same and even more.
Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU) is an automated feature that allows you to update clustered servers with little or no loss in availability during the update process. During an Updating Run, CAU transparently performs the following tasks:
- Puts each node of the cluster into node maintenance mode
- Moves the clustered roles off the node
- Installs the updates and any dependent updates
- Performs a restart if necessary
- Brings the node out of maintenance mode
- Restores the clustered roles on the node
- Moves to update the next node
Microsoft TechNet: Cluster-Aware Updating overview
CAU does not only move Virtual Machines, like SCVMM, it does also know about other Cluster Roles like Hyper-V Replica Broker or File shares.
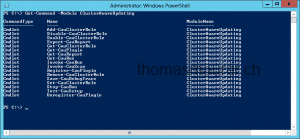
To use or configure Cluster-Aware Updating you have to install the RSAT for Clustering via GUI or via Windows PowerShell:
Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-Clustering
After this you can run the Cluster-Aware Updating tool via GUI or the new Windows PowerShell module.
Using Cluster-Aware Updating
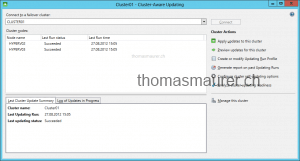
In the Cluster-Aware Updating console you have different options.
- Apply updates to this cluster – Manually start updating process for a specific cluster
- Preview updates for this cluster – Check which updates will be installed
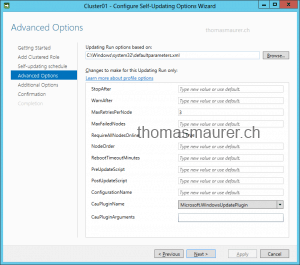
- Create or modify Updating Run Profile – Lets you configure the default settings for the Updating Run Profile
- Generate report on past Updating Runs
- Configure cluster self-updating options – Lets you configure and schedule the updating process for a specific cluster.
- Analyze cluster updating readiness – Analyzes your cluster and roles so the cluster can be patched without downtime.
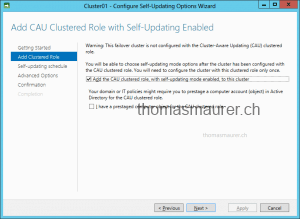
Configure cluster self-updating options
CAU can be scheduled to updates clusters without any manual action.
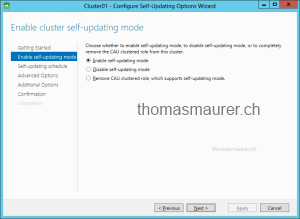
First choose the cluster and enable the self-updating feature on the cluster
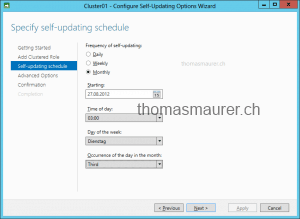
Specify the self-updating schedule
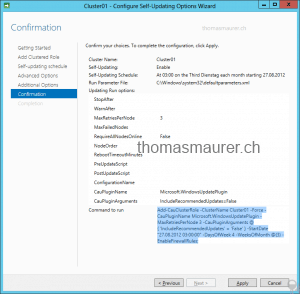
Specify the updating options
Save the scheduled self-updating process
After you have configured the self-updating process you can still modify it.
I hope this gives you a small insight into Cluster-Aware Updating and self-updating for Clusters. If you run some Clusters with 16 nodes you know how much time was needed for manually updating the cluster nodes. With Windows Server 2012 the new maximum number of nodes in a cluster is 64, so CAU will save administrators a lot of time and will keep your clusters up to date.
For more information about Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU) check out Microsoft TechNet.
Tags: CAU, Cluster, Cluster Updating, Cluster-Aware Updating, Hyper-V, Microsoft, PowerShell, SCCM, SCVMM, Self-Updating, VMM, Windows Server, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V, Windows Update, WSUS Last modified: January 7, 2019









hi!
could you let me know what the prerequirements for Hyper-V and CAU are?
do you have to have all Hyper-V hosts connect to one CSV where all guests are?
thanks in advance!
I would imagine you don’t have to have all VMs in CSVs but that means when it starts moving all your resources before putting the node in maintenance mode, they will be paused and moved rather to live migration where there is no downtime. All your VMs would need to be in the cluster though.
Hi, Can CAU work with our SCCM 2007 R3 Server?